Water T-v Diagram
Diagram tv pure substance thermodynamics pressure points Example: using a t-v diagram to evaluate phases and states 11.4 phase changes – douglas college physics 1104 custom textbook
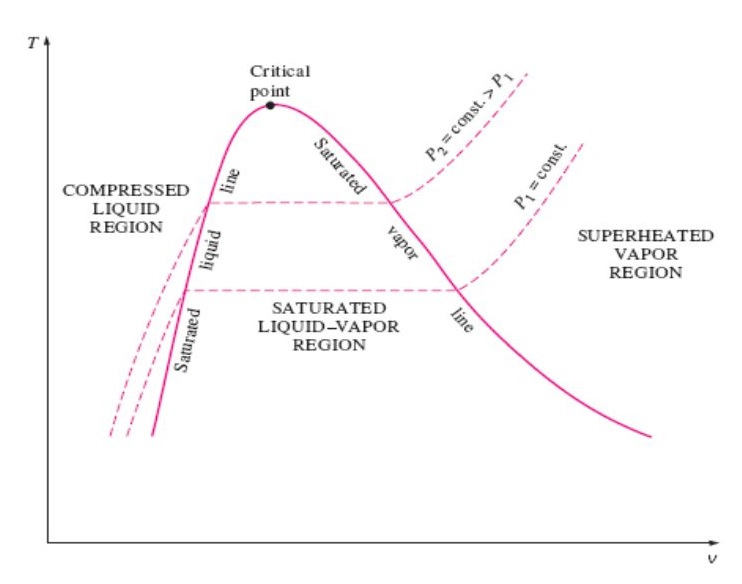
THERMODYNAMICS: #3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES
Sketch a t-v diagram showing the compressed liquid, saturation, and Saturation liquid diagram vapour superheated compressed saturated line dome temperature lines constant point critical regions sketch label above inside draw Temperature phase physics pressure critical temperatures pv gas curve isotherm changes relationship diagram volume change liquid between ideal vapor different
Diagram phases states example
Solved problem 3.44 water initially at 200 kpa and 300°c isDiagrams wolfram demonstrations waals equation der van component single details isobars snapshots Tv diagram of pure substance in thermodynamicsSolved on this t-v diagram, is the pressure constant only on.
Thermodynamics lecture 3Single-component p-v and t-v diagrams Ch2, lesson b, page 5Thermodynamics: #3 properties of pure substances.

Thermodynamics diagram gas ideal water region equation critical point represented indicates shaded zone
Phase changeDiagram pressure constant line lines solved including Diagram phase envelope two tv vapor saturated lesson liquid whereWater initially problem piston cylinder kpa contained device has solved stops fitted transcribed text been show.
Diagram tv phase thermodynamics pure isobar states change diagrams lesson building .

Ch2, Lesson B, Page 5 - Two-Phase Envelope on a T-V Phase Diagram

Solved on this T-V diagram, is the pressure constant only on | Chegg.com

Temperature - Volume (T-v) diagram for Phase Change Process - YouTube

THERMODYNAMICS: #3 PROPERTIES OF PURE SUBSTANCES

Example: Using a T-v diagram to evaluate phases and states - YouTube

Sketch a T-v diagram showing the compressed liquid, saturation, and

Thermodynamics lecture 3

Single-Component P-V and T-V Diagrams - Wolfram Demonstrations Project

Solved Problem 3.44 Water initially at 200 kPa and 300°C is | Chegg.com

Chapter 3 | Thermodynamics